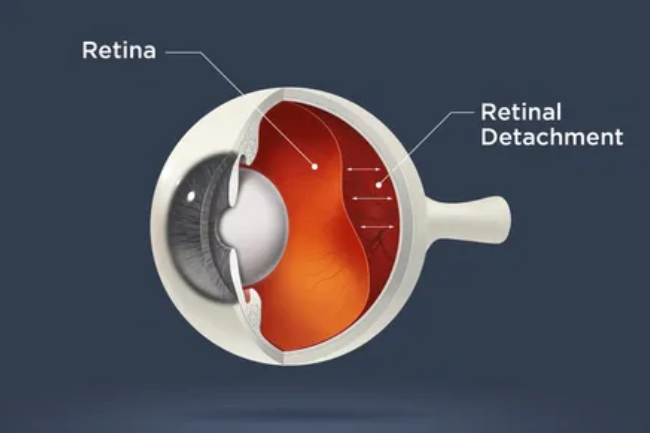
The retina is a thin layer of tissue located at the back of the eye that plays a crucial role in vision. It contains specialized cells called photoreceptors that detect light and convert it into electrical signals that are sent to the brain through the optic nerve. These electrical signals are then processed by the brain into visual images. The retina also contains other important cells, such as retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells and ganglion cells, which play essential roles in maintaining retinal health and transmitting visual information. The retina is vital for clear vision and is responsible for processing and transmitting visual information to the brain for perception.
Retinal Disorders
What is Retina?
Diabetic Retinopathy
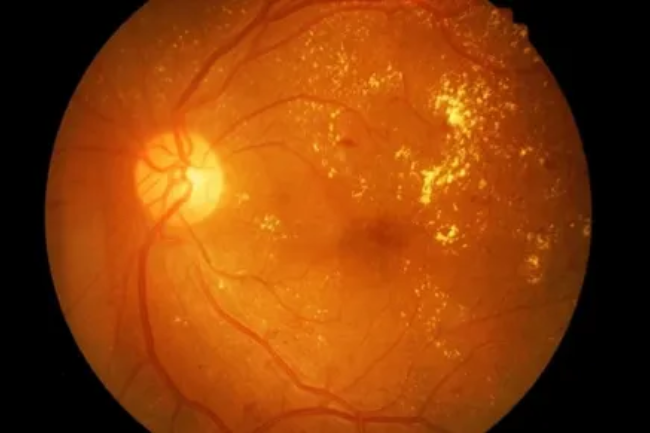
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that occurs in people with diabetes. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. High blood sugar levels in diabetes can weaken and damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to various stages of diabetic retinopathy, ranging from mild to severe. Diabetic retinopathy can cause vision loss or even blindness if left untreated. Common symptoms may include blurry vision, floaters, dark spots or patches, and difficulty seeing at night. Regular eye examinations and tight control of blood sugar levels are crucial for early detection and management of diabetic retinopathy. Treatment options may include laser therapy, intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF medications, and, in advanced cases, vitrectomy surgery. Early detection, appropriate management, and good glycemic control are key in preventing or minimizing the impact of diabetic retinopathy on vision.
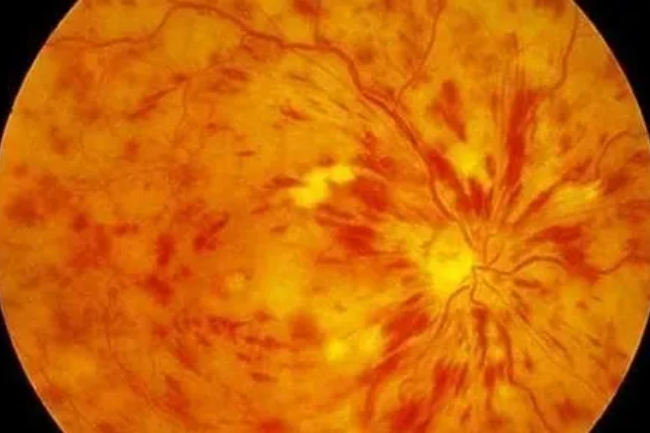
Retinal Vascular occlusions
Retinal vascular occlusions, also known as retinal vein occlusion or retinal artery occlusion, are conditions that occur when the blood flow to the retina is blocked due to a clot or other vascular obstruction. This can result in damage to the retina, leading to vision loss. Retinal vascular occlusions can be caused by various factors, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and other underlying medical conditions. Common symptoms may include sudden, painless vision loss in one eye, blurry or distorted vision, and dark spots or floaters in the vision. Treatment options may include medications to manage underlying conditions, laser therapy, and in some cases, intravitreal injections or surgical interventions. Early diagnosis and management are important to prevent further vision loss and preserve retinal health. Regular eye examinations and managing risk factors can help reduce the risk of retinal vascular occlusions.
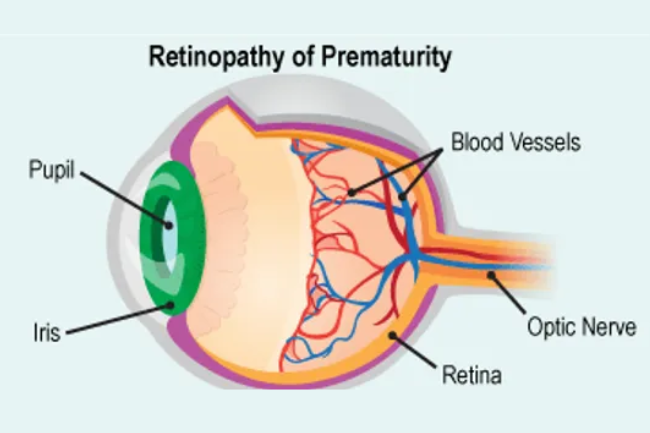
Retinopathy of Prematurity
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is a condition that affects premature infants, particularly those born before 31 weeks of gestation or with a birth weight less than 1500 grams. ROP occurs due to abnormal blood vessel growth in the developing retina, which can lead to scarring and retinal detachment, potentially causing vision loss or blindness if left untreated. ROP is typically screened for and monitored in premature infants through specialized eye examinations. Treatment options may include laser therapy, cryotherapy, or, in severe cases, vitrectomy surgery. Early detection, appropriate management, and close follow-up are essential in preventing or minimizing the impact of ROP on visual outcomes in premature infants.
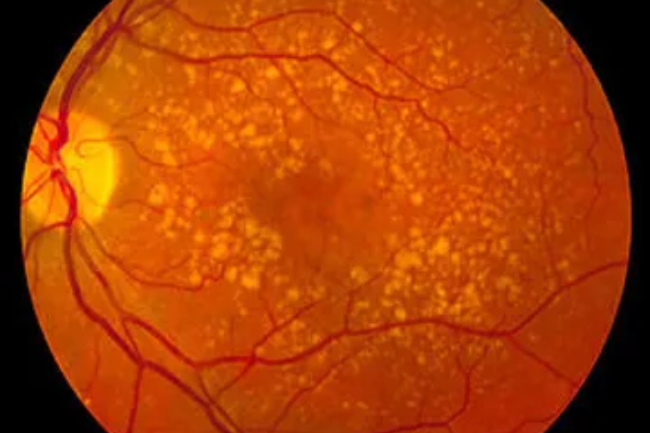
Age Related Macular Degenerations
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common eye condition that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision. AMD typically occurs in individuals aged 50 years and older and is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. AMD can be classified as either dry (atrophic) or wet (neovascular) AMD. Dry AMD is characterized by the gradual breakdown of the macular tissue, while wet AMD involves the growth of abnormal blood vessels beneath the retina. Common symptoms may include blurry or distorted central vision, dark or empty spots in the vision, and difficulty with tasks that require sharp central vision, such as reading or driving. There is currently no cure for AMD, but treatment options such as intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF medications, laser therapy, and nutritional supplements may be used to manage the condition and slow its progression. Early detection, regular eye examinations, and lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding smoking, are crucial in managing AMD and preserving vision in older adults.
Retinal Detachments
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that occurs when the retina, the thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye, becomes detached from its normal position. This can result in vision loss or blindness if left untreated. Retinal detachment may be caused by various factors, such as trauma, aging, or underlying eye conditions. Common symptoms may include sudden onset of floaters, flashes of light, or a curtain-like shadow in the peripheral or central vision. Treatment options may include surgical interventions, such as vitrectomy or scleral buckle, to reattach the retina and restore vision. Early detection, prompt medical attention, and timely surgical intervention are critical in preserving vision in cases of retinal detachment.