Refractive errors are common vision problems that occur when the shape of the eye prevents light from properly focusing onto the retina, leading to blurred vision. There are four main types of refractive errors: myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), astigmatism (irregular corneal curvature), and presbyopia (age-related loss of near vision). Myopia causes distant objects to appear blurry, while hyperopia makes close-up objects blurry. Astigmatism causes overall blurred vision at all distances, and presbyopia affects near vision, particularly in those over 40 years old. Refractive errors can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery such as LASIK. Regular eye examinations and appropriate correction can help manage refractive errors and maintain clear vision.
Pediatric Ophthalmology

Refractive errors
Amblyopia
Amblyopia, commonly known as “lazy eye,” is a condition that occurs when the visual acuity in one eye is significantly reduced compared to the other eye, even with the use of glasses or contact lenses. It typically develops during childhood when the visual system is still developing and can result from factors such as strabismus (misaligned eyes), significant difference in refractive errors between the two eyes, or other eye conditions that interfere with clear vision. If left untreated, amblyopia can cause permanent visual impairment. Early detection and treatment, such as patching the stronger eye or using eye drops to blur vision in the stronger eye, can help improve visual outcomes in amblyopic children. Regular eye examinations during childhood are crucial in detecting and managing amblyopia.

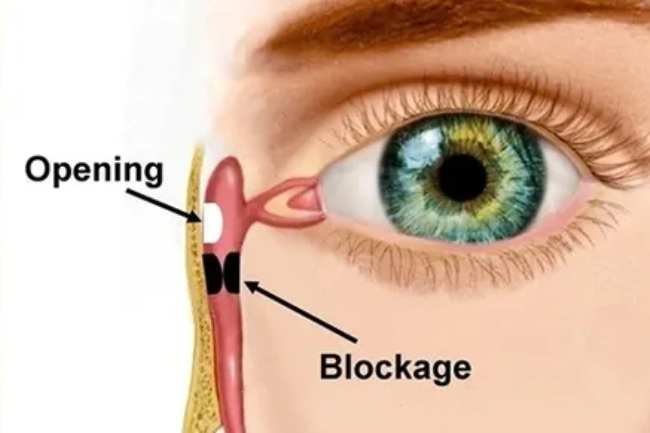
NLD Obstruction
Nasolacrimal duct (NLD) obstruction is a condition that occurs when there is a blockage in the drainage system of tears from the eye to the nose. This can result in tearing, eye discharge, and eye infections. NLD obstruction is commonly seen in infants and young children, but it can also occur in adults. It can be caused by various factors, including congenital abnormalities, trauma, infections, or inflammation. Treatment options for NLD obstruction depend on the severity and cause of the blockage and may include conservative measures such as warm compresses and massage, or more invasive interventions like probing or surgery to open the blocked tear duct. Proper diagnosis and management by an eye care professional is important to prevent complications and maintain eye health.
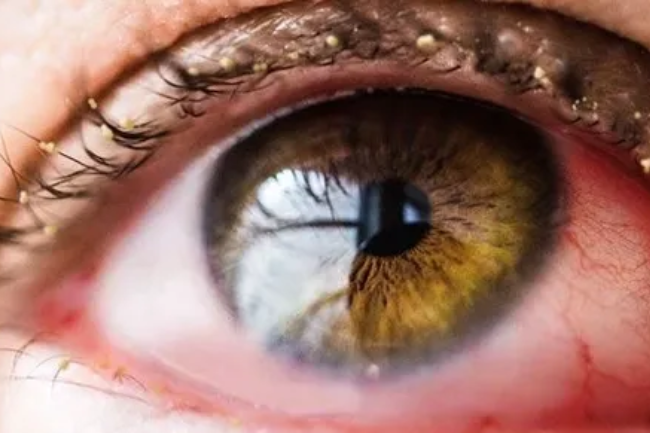
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane that covers the whites of the eyes and the inner surface of the eyelids, due to an allergic reaction. It is a common condition that can cause symptoms such as redness, itching, tearing, and swollen eyelids. Allergic conjunctivitis is usually triggered by allergens such as pollen, pet dander, dust mites, or mold spores. Avoiding allergens and using artificial tears or antihistamine eye drops can help relieve mild symptoms. In more severe cases, corticosteroid eye drops or other medications may be prescribed by an eye care professional. Proper identification and management of the underlying allergens are essential for effective control of allergic conjunctivitis.
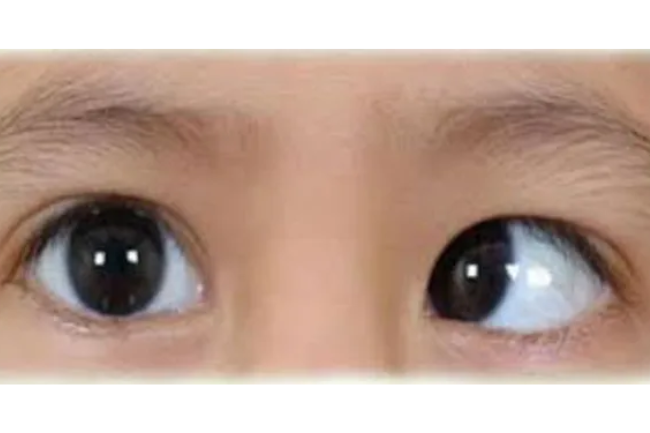
Squint
Squint, also known as strabismus, is a condition in which the eyes do not align properly and do not move in coordination. This can result in one eye appearing to be misaligned or deviated in relation to the other eye. Squint can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired later in life due to various factors such as muscle imbalance, neurological conditions, trauma, or other eye conditions. Squint can lead to visual impairment, double vision, and social and psychological impact. Treatment options for squint include corrective glasses, patching, eye exercises, or surgical intervention to align the eyes properly. Early diagnosis and management by an eye care professional are important to prevent long-term complications and improve visual outcomes.
Congenital Cataract and Glaucoma
Congenital cataract and glaucoma are two eye conditions that can affect infants and young children.
Congenital cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye that is present at birth or develops during infancy. It can cause visual impairment or blindness if not detected and treated early. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the cataract and implantation of an intraocular lens (IOL) to restore vision.
Glaucoma is a condition characterized by increased intraocular pressure (IOP) that can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss if left untreated. Congenital glaucoma is a rare form of glaucoma that is present at birth or develops during infancy. It requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent visual impairment or blindness. Treatment options may include medications, laser therapy, or surgery to lower the IOP and preserve vision.
Early detection, timely intervention, and regular follow-up with an eye care professional are crucial in managing congenital cataract and glaucoma in children to optimize visual outcomes and ensure proper eye health.