The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped outermost layer of the eye that covers the front part of the eye, including the iris and the pupil. It acts as a protective barrier against dust, debris, and germs, and helps to focus light entering the eye onto the lens and retina for clear vision. The cornea is composed of multiple layers of transparent tissue, including the epithelium, stroma, and endothelium. It is responsible for most of the eye’s refractive power, meaning it plays a crucial role in the eye’s ability to focus light and create sharp images on the retina. The cornea is also highly sensitive and densely innervated, making it vital for maintaining corneal integrity and visual acuity.
Corneal Transplant
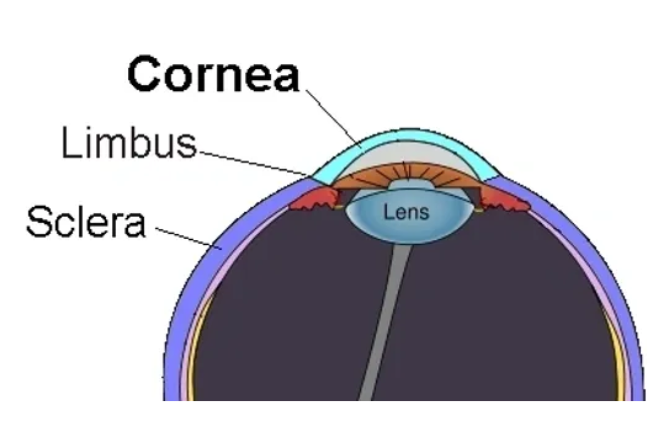
What is Cornea?
Corneal Transplant
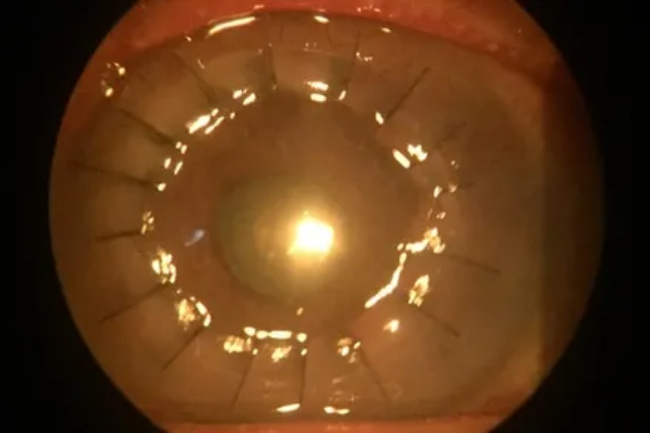
Corneal transplant, also known as corneal transplantation or keratoplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged or diseased cornea with a healthy cornea from a donor. The cornea is a clear, dome-shaped tissue on the front of the eye that plays a crucial role in vision. Corneal transplants are typically performed to restore vision in cases where the cornea is damaged due to conditions such as corneal scars, corneal degeneration, corneal ulcers, or keratoconus. The procedure involves removing the damaged cornea and replacing it with a donated cornea, which is carefully matched for size, shape, and compatibility. Corneal transplant can significantly improve vision and quality of life for patients with corneal conditions that cannot be managed with other treatments.
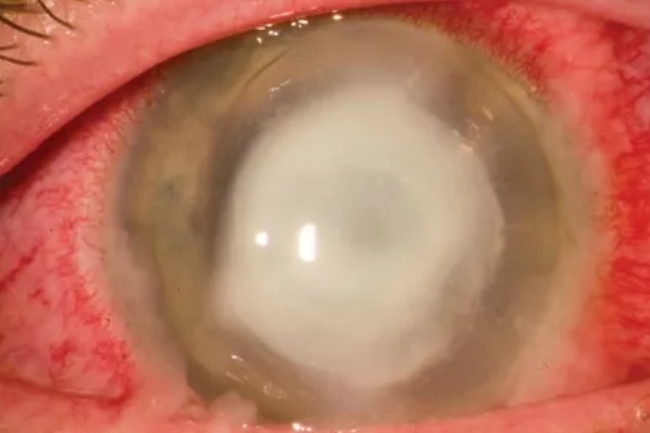
Corneal Ulcer
A corneal ulcer is a painful and potentially serious condition that involves the formation of an open sore or ulcer on the surface of the cornea, which is the clear, dome-shaped outer layer of the eye. Corneal ulcers can be caused by various factors, including bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, trauma, dry eye syndrome, contact lens-related complications, or other underlying eye conditions. Symptoms may include eye pain, redness, blurred vision, tearing, light sensitivity, and discharge from the eye. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent further damage to the cornea and potential vision loss. Treatment may include antibiotic, antiviral, or antifungal eye drops, lubricating eye drops, pain management, and sometimes, patching or bandage contact lenses. Severe cases may require corneal debridement, surgical intervention, or corneal transplant.
Dry Eyes and Computer Vision Syndrome
Dry eyes and computer vision syndrome (CVS) are related eye conditions that can occur due to prolonged use of digital devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. Dry eyes occur when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too quickly, leading to discomfort, redness, burning, and blurred vision. CVS, also known as digital eye strain, refers to a group of eye and vision-related symptoms caused by prolonged digital device use, including eye strain, eye fatigue, dryness, discomfort, headaches, and blurred vision. Both dry eyes and CVS can be managed through measures such as taking regular breaks, practicing the 20-20-20 rule (looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes), adjusting screen settings, using artificial tears or lubricating eye drops, maintaining good blinking habits, optimizing ergonomics, and practicing good eye hygiene. Consultation with an eye care professional is recommended for proper diagnosis and management of these conditions.

Corneal Degeneration
Corneal degeneration refers to the gradual deterioration or weakening of the cornea, which is the clear, dome-shaped outer layer of the eye. Corneal degeneration can occur due to various factors, including aging, genetic predisposition, previous eye injuries or surgeries, systemic conditions such as diabetes, and environmental factors such as UV radiation. Corneal degeneration can result in vision changes, such as blurred or distorted vision, sensitivity to light, and decreased visual acuity. Treatment options for corneal degeneration depend on the severity of the condition and may include conservative measures such as using lubricating eye drops, wearing protective eyewear, and managing underlying systemic conditions. In more advanced cases, surgical interventions such as corneal cross-linking, corneal transplantation, or other specialized procedures may be recommended by an eye care professional. Early detection and management are key to preserving vision in cases of corneal degeneration.
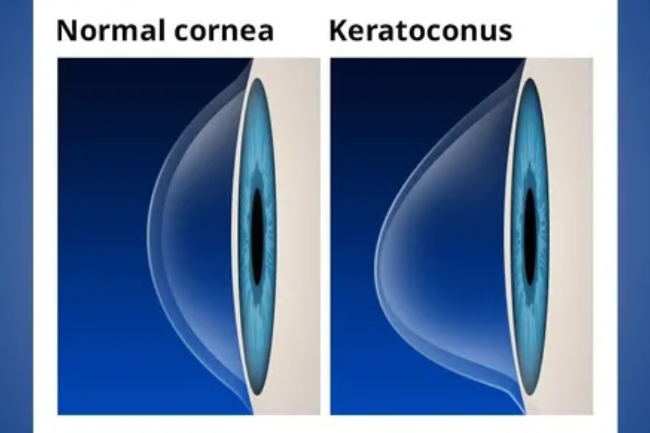
Keratoconus
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disorder that causes thinning and bulging of the cornea, resulting in a cone-like shape instead of the normal dome shape. This irregular corneal shape can cause significant vision problems, including blurred or distorted vision, sensitivity to light, glare, and frequent changes in prescription for glasses or contact lenses. Keratoconus typically starts during teenage years or early adulthood and may worsen over time. Treatment options for keratoconus include glasses or contact lenses for mild cases, while more advanced cases may require corneal cross-linking, intracorneal ring segments, or corneal transplantation. Regular monitoring by an eye care professional and early intervention can help manage the progression of keratoconus and optimize visual outcomes.